Abstract
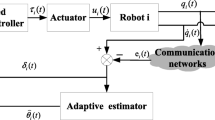
In this paper, to solve the consensus control problem of multi-manipulator systems under Markov switching topologies, we propose a distributed consensus control strategy based on disturbance observer. In multi-manipulator systems, external disturbance described by heterogeneous exogenous systems is considered, and all communication topologies are directed. First, a disturbance observer is presented to suppress the influence of unknown external disturbance, and the equivalent compensation is introduced into the control protocol in multi-manipulator systems. Then, a novel control protocol based on neighbor information is designed, which guarantees that multi-manipulator systems reach consensus under Markov switching topologies. Finally, two simulation examples verify the validity of the theoretical result.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, C. L. P., Wen, G. X., Liu, Y. J., & Liu, Z. (2016). Observer-based adaptive backstepping consensus tracking control for high-order nonlinear semi-strict-feedback multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 46(7), 1591–1601.
Du, H. B., Cheng, Y. Y., He, Y. G., & Jia, R. T. (2016). Second-order consensus for nonlinear leader-following multi-agent systems via dynamic output feedback control. International Journal of Robust & Nonlinear Control, 26(2), 329–344.
Li, G., Ren, C. E., Chen, C. P., & Shi, Z. (2020). Adaptive iterative learning consensus control for second-order multi-agent systems with unknown control gains. Neurocomputing, 393, 15–26.
Ren, C. E., & Chen, C. L. P. (2015). Sliding mode leader-following consensus controllers for second-order non-linear multi-agent systems. IET Control Theory and Applications, 9(10), 1544–1552.
Ren, C. E., Chen, C. L. P., Du, T., & Guan, Y. (2019). Fuzzy adaptive leader-following consensus control for nonlinear multi-agent systems with unknown control directions. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 21(7), 2066–2076.
Zhang, X. X., Zhu, Q. D., & Liu, X. P. (2016). Consensus of second order multi-agent systems with exogenous disturbance generated by unknown exosystems. Entropy, 18(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/e18120423.
Zuo, Z. Y., & Tie, L. (2016). Distributed robust finite-time nonlinear consensus protocols for multi-agent systems. International Journal of Systems Science, 47(6), 1366–1375.
Fateh, S., & Fateh, M. M. (2020). Adaptive fuzzy control of robot manipulators with asymptotic tracking performance. Journal of Control, Automation and Electrical Systems, 31(1), 52–61.
Yu, S. H., Yu, X. H., Shirinzadeh, B., & Man, Z. H. (2005). Continuous finite-time control for robotic manipulators with terminal sliding mode. Automatica, 41(11), 1957–1964.
Zhao, D. Y., Ni, W., & Zhu, Q. M. (2014). A framework of neural networks based consensus control for multiple robotic manipulators. Neurocomputing, 140, 8–18.
Zhao, G., & Zhao, D.Y. (2014). Robust consensus control for multiple robotic manipulators. In: Proceedings of the33rd Chinese Control Conference (CCC) (pp. 2229-2233). Nanjing, China.
Yu, W.W., Chen, G. R., Cao, M., & Kurths, J. (2010). Second-order consensus for multiagent systems with directed topologies and nonlinear dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics – Part B: Cybernetics, 40(3), 881–891.
Defoort, M., Polyakov, A., Demesure, G., Djemai, M., & Veluvolu, K. C. (2015). Leader-follower fixed-time consensus for multi-agent systems with unknown nonlinear inherent dynamics. IET Control Theory & Applications, 9(14), 2165–2170.
Du, H. B., Li, S. H., & Shi, P. (2012). Robust consensus algorithm for second-order multi-agent systems with external disturbances. International Journal of Control, 85(12), 1913–1928.
Gong, P., & Lan, W. Y. (2018). Adaptive robust tracking control for uncertain nonlinear fractional-order multi-agent systems with directed topologies. Automatica, 92, 92–99.
Zhao, D., Zou, T., Li, S., & Zhu, Q. (2012). Adaptive backstepping sliding mode control for leader-follower multi-agent systems. IET Control Theory & Applications, 6(8), 1109–1117.
Tong, S.C., & Li, Y. (2014). Observer-based adaptive fuzzy backstepping control of uncertain nonlinear pure-feedback systems. Science China-Information Sciences, 57(1), 203–216.
Tong, S.C., & Li, Y.M. (2010). Robust adaptive fuzzy backstepping output feedback tracking control for nonlinear system with dynamic uncertainties. Science China-Information Sciences, 53(2), 97–114.
Wu, Z. H., & Guo, B. Z. (2016). Extended state observer for uncertain lower triangular nonlinear systems subject to stochastic disturbance. Control Theory and Technology, 14(3), 179–188.
Zheng, Q., & Gao, Z. (2018). Active disturbance rejection control: some recent experimental and industrial case studies. Control Theory and Technology, 16(4), 301–313.
Lee, T. H., Park, J. H., Ji, D. H., & Jung, H. Y. (2014). Leader-following consensus problem of heterogeneous multi-agent systems with nonlinear dynamics using fuzzy disturbance observer. Complexity, 19(4), 20–31.
Wang, X. Y., Li, S. H., & Lam, J. (2016). Distributed active anti-disturbance output consensus algorithms for higher-order multi-agent systems with mismatched disturbances. Automatica, 74, 30–37.
Cheng, B., Wang, X. K., & Li, Z. K. (2019). Event-triggered consensus of homogeneous and heterogeneous multiagent systems with jointly connected switching topologies. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 49(12), 4421–4430.
Jiang, J. H., & Jiang, Y. Y. (2020). Leader-following consensus of linear time-varying multi-agent systems under fixed and switching topologies. Automatica, 113, 108804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.automatica.2020.108804.
Wang, P. J., Hui, W. G., Yu, X. H., Yu, W. W., & Lv, Y. Z. (2020). Consensus disturbance rejection for linear multiagent systems with directed switching communication topologies. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 7(1), 254–265.
Wang, R. (2020). Adaptive output-feedback time-varying formation tracking control for multi-agent systems with switching directed networks. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 357(1), 551–568.
Xing, M. L., & Deng, F. Q. (2019). Adaptive cooperative tracking control of uncertain nonlinear multiagent systems with uncertain Markov switching communication graphs. International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing, 33(3), 1506–1523.
Zhao, D. Y., Zhu, Q. M., Li, N., & Li, S. Y. (2014). Synchronized control with neuro-agents for leader-follower based multiple robotic manipulators. Neurocomputing, 124, 149–161.
Ren, C. E., Du, T., Li, G. L., & Shi, Z. P. (2018). Disturbance observer-based consensus control for multiple robotic manipulators. IEEE Access, 6, 51348–51354.
Horn, R. A., & Johnson, C. R. (2012). Matrix Analysis. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
You, K., Li, Z., & Xie, L. (2013). Consensus condition for linear multi-agent systems over randomly switching topologies. Automatica, 49(10), 3125–3132.
Wang, D., Wang, D., Wang, W., Liu, Y. R., & Alsaadi, F. E. (2017). Distributed optimisation for multi-agent systems with the first-order integrals under Markovian switching topologies. International Journal of Systems Science, 48(9–12), 1787–1795.
Fragoso, M. D., & Costa, O. L. V. (2005). A unified approach for stochastic and mean square stability of continuous-time linear systems with Markovian jumping parameters and additive disturbances. SIAM Journal on Control & Optimization, 44(4), 1165–1191.
Chen, W. H. (2004). Disturbance observer based control for nonlinear systems. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 9(4), 706–710.
Liu, L., Liang, X.L., & Zhang, J.Q. (2018). Consensus control for second order multi-agent system with switching interaction topologies. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Project Management (pp. 640–645). Chongqing, China.
Ni, W., & Cheng, D. Z. (2010). Leader-following consensus of multi-agent systems under fixed and switching topologies. Systems & Control Letters, 59(3–4), 209–217.
Cheng, L., Hou, Z.G., & Tan, M. (2008). Decentralized adaptive consensus control for multi-manipulator system with uncertain dynamics. In: IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (pp. 2712–2717). Singapore.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61803276), the Beijing Municipal Education Commission Science Plan (General Research Project, No. KM201910028004), the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. 4202011), and Key Research Grant of Academy for Multidisciplinary Studies of CNU (No. JCKXYJY2019018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, CE., Fu, Q. Consensus control of multi-manipulator systems based on disturbance observer under Markov switching topologies. Control Theory Technol. 19, 273–282 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11768-020-00028-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11768-020-00028-6