Abstract
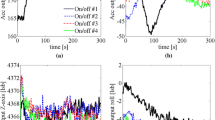
MEMS (micro-electro-mechanical-system) IMU (inertial measurement unit) sensors are characteristically noisy and this presents a serious problem to their effective use. The Kalman filter assumes zero-mean Gaussian process and measurement noise variables, and then recursively computes optimal state estimates. However, establishing the exact noise statistics is a non-trivial task. Additionally, this noise often varies widely in operation. Addressing this challenge is the focus of adaptive Kalman filtering techniques. In the covariance scaling method, the process and measurement noise covariance matrices Q and R are uniformly scaled by a scalar-quantity attenuating window. This study proposes a new approach where individual elements of Q and R are scaled element-wise to ensure more granular adaptation of noise components and hence improve accuracy. In addition, the scaling is performed over a smoothly decreasing window to balance aggressiveness of response and stability in steady state. Experimental results show that the root mean square errors for both pith and roll axes are significantly reduced compared to the conventional noise adaptation method, albeit at a slightly higher computational cost. Specifically, the root mean square pitch errors are 1.1\(^\circ\) under acceleration and 2.1\(^\circ\) under rotation, which are significantly less than the corresponding errors of the adaptive complementary filter and conventional covariance scaling-based adaptive Kalman filter tested under the same conditions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vidal, A. R., Rebecq, H., Horstschaefer, T., & Scaramuzza, D. (2018). Ultimate SLAM? Combining events, images, and IMU for robust visual SLAM in HDR and high-speed scenarios. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 3(2), 994–1001.
Randeniya, D. I., Sarkar, S., & Gunaratne, M. (2010). Vision-IMU integration using a slow-frame-rate monocular vision system in an actual roadway setting. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 11(2), 256–266.
Ates, S., Haarman, C. J., & Stienen, A. H. (2017). SCRIPT passive orthosis: design of interactive hand and wrist exoskeleton for rehabilitation at home after stroke. Autonomous Robots, 41(3), 711–723.
Tupysev, V. A., Stepanov, O. A., Loparev, A. V., & Litvinenko, Y. A. (2009). Guaranteed estimation in the problems of navigation information processing. In 2009 IEEE Control Applications, (CCA) & Intelligent Control, (ISIC), St Petersburg, Russia, pp. 1672–1677.
Mehra, R. (1972). Approaches to adaptive filtering. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 17(5), 693–698.
Tupysev, V., Kruglova, N., & Motorin, A. (2017). Suboptimal algorithms for identification of navigation sensor errors described by Markov process. Gyroscopy and Navigation, 8(1), 58–62.
Yan, J., Yuan, D., Xing, X., & Jia, Q. (2008). Kalman filtering parameter optimization techniques based on genetic algorithm. In 2008 IEEE International Conference on Automation and Logistics, Qingdao, China, pp. 1717–1720.
Liu, Z., Guo, W., Tang, Z., & Chen, Y. (2015). Multi-sensor data fusion using a relevance vector machine based on an ant colony for gearbox fault detection. Sensors, 15(9), 21857–21875.
Vargas-Meléndez, L., Boada, B. L., Boada, M. L., Gauchía, A., & Díaz, V. (2016). A sensor fusion method based on an integrated neural network and Kalman filter for vehicle roll angle estimation. Sensors, 16(9), 1400.
Al Bitar, N., Gavrilov, A., & Khalaf, W. (2020). Artificial intelligence based methods for accuracy improvement of integrated navigation systems during GNSS signal outages: An analytical overview. Gyroscopy and Navigation, 11, 41–58.
Wang, J., Stewart, M., & Tsakiri, M. (1999). Online stochastic modelling for INS/GPS integration. In Proceedings of the 12th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GPS 1999), Nashville, TN, USA, pp. 1887–1896.
Mohamed, A., & Schwarz, K. (1999). Adaptive Kalman filtering for INS/GPS. Journal of Geodesy, 73(4), 193–203.
Busse, F. D., How, J. P., & Simpson, J. (2003). Demonstration of adaptive extended Kalman filter for low-earth-orbit formation estimation using CDGPS. NAVIGATION, Journal of the Institute of Navigation, 50(2), 79–94.
Li, X. R., & Jilkov, V. P. (2005). Survey of maneuvering target tracking—Part V: Multiple-model methods. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 41(4), 1255–1321.
Huang, Y., Zhang, Y., Wu, Z., Li, N., & Chambers, J. (2017). A novel adaptive Kalman filter with inaccurate process and measurement noise covariance matrices. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 63(2), 594–601.
Hu, C., Hu, X., & Hong, Y. (2019). Distributed adaptive Kalman filter based on variational Bayesian technique. Control Theory and Technology, 17(1), 37–47.
Sage, A. P. & Husa, G. W. (1969). Algorithms for sequential adaptive estimation of prior statistics. In 1969 IEEE Symposium on Adaptive Processes (8th) Decision and Control, University Park, PA, USA, pp. 61.
Narasimhappa, M., Rangababu, P., Sabat, S. L., & Nayak, J. (2012). A modified sage-husa adaptive Kalman filter for denoising fiber optic gyroscope signal. In 2012 Annual IEEE India Conference (INDICON), Kochi, India, pp. 1266–1271.
Xia, Q., Rao, M., Ying, Y., & Shen, X. (1994). Adaptive fading Kalman filter with an application. Automatica, 30(8), 1333–1338.
Jwo, D.-J., & Wang, S.-H. (2007). Adaptive fuzzy strong tracking extended Kalman filtering for GPS navigation. IEEE Sensors Journal, 7(5), 778–789.
Zhang, A., Shuida, B., Fei, G., & Wenhao, B. (2019). A novel strong tracking cubature Kalman filter and its application in maneuvering target tracking. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 32(11), 2489–2502.
Liu, Y., Fan, X., Lv, C., Wu, J., Li, L., & Ding, D. (2018). An innovative information fusion method with adaptive Kalman filter for integrated INS/GPS navigation of autonomous vehicles. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 100, 605–616.
Ding, W., Wang, J., Rizos, C., & Kinlyside, D. (2007). Improving adaptive Kalman estimation in GPS/INS integration. The Journal of Navigation, 60(3), 517.
Almagbile, A., Wang, J., & Ding, W. (2010). Evaluating the performances of adaptive Kalman filter methods in GPS/INS integration. Journal of Global Positioning Systems, 9(1), 33–40.
Wang, J. (1999). Stochastic modeling for real-time kinematic GPS/GLONASS positioning. Navigation, 46(4), 297–305.
InvenSense. (2016). Technical documentation for MPU-9250. https://invensense.tdk.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/PS-MPU-9250A-01-v1.1.pdf. Accessed 12 Feb 2019.
Schneider, R., & Georgakis, C. (2013). How to not make the extended Kalman filter fail. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 52(9), 3354–3362.
Boyd, S., & Xiao, L. (2005). Least-squares covariance matrix adjustment. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 27(2), 532–546.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mumuni, F., Mumuni, A. Adaptive Kalman filter for MEMS IMU data fusion using enhanced covariance scaling. Control Theory Technol. 19, 365–374 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11768-021-00058-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11768-021-00058-8